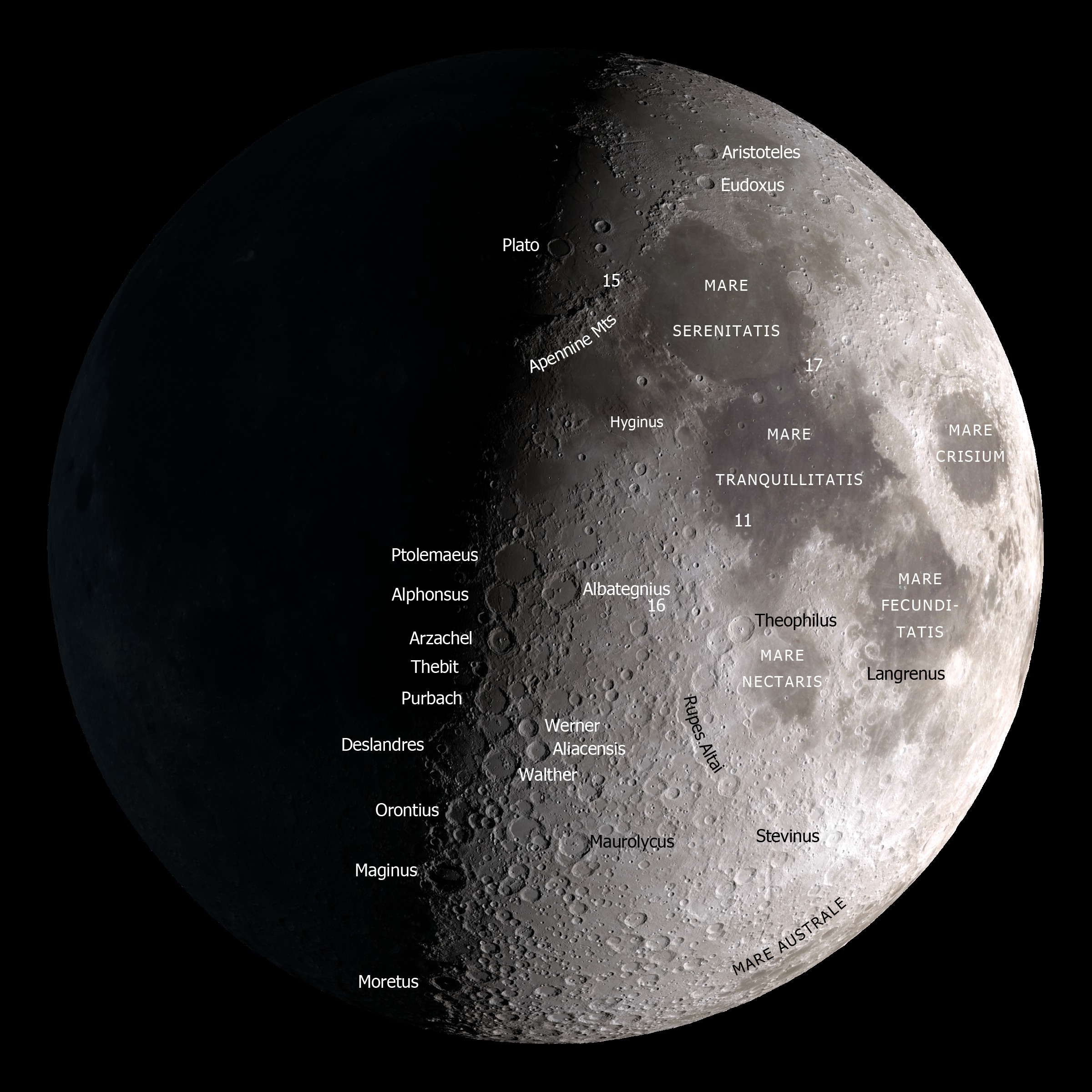


Z factor vertical exaggeration – used to emphasise vertical features especially where they might be too small to identify relative to the horizontal scale.QGIS has a great GDAL hill shade option that allows you to import your raster (DEM) and output a shaded relief effect based on the parameters you set in the dialogue box. I chose an area of 1350km by 1000km at a scale of 1:1,470,000 and clipped from the original DEM before using it to create hill shade. Next, I located the lunar landing site of Apollo 11 and worked out the extent of the moon around it that I wanted to map. The DEM was projected using the Moon 2000 projection (IAU 2000:30100).
LUNAR LANDING MAP SOFTWARE
From this DEM we were able to create a terrain representation using Geographic Information Software (GIS).Īfter a few issues trying to download the DEM due to the United States Federal Government shutdown, I was eventually able to load it into a GIS, in this case QGIS. The United States Geological Survey (USGS) have a 60 metre per pixel DEM which was created by NASA’s LOLA Team and JAXA’s SELENE/Kaguya Team. The good news is there are lots of Digital Elevation Model’s or DEM’s of the Moon, which are 3D representations of a terrain’s surface.

The first step in creating a map of the Moon is to identify available data that represents the Moon’s topography. Eventually a site within the Sea of Tranquility was chosen.
LUNAR LANDING MAP FREE
The original requirement that the site be free of craters had to be relaxed.
This year marks the 50 th year anniversary of the moon landing, and to celebrate and mark the occasion the OS GeoDataViz team thought it would be fitting to create a map of Apollo 11’s lunar landing site in our unique map style.Find out how Paul Naylor approached the task.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
